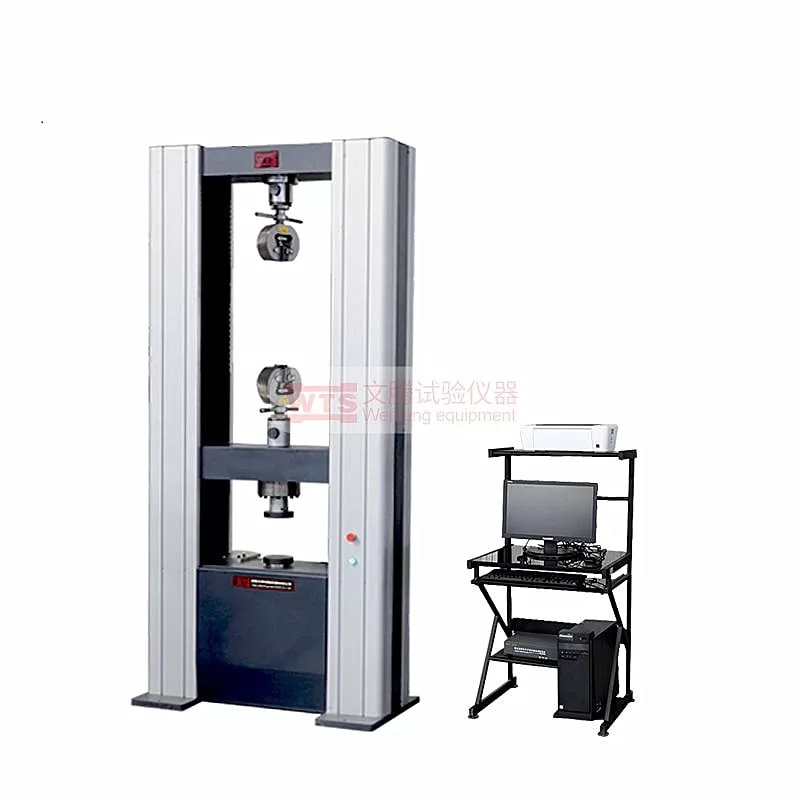
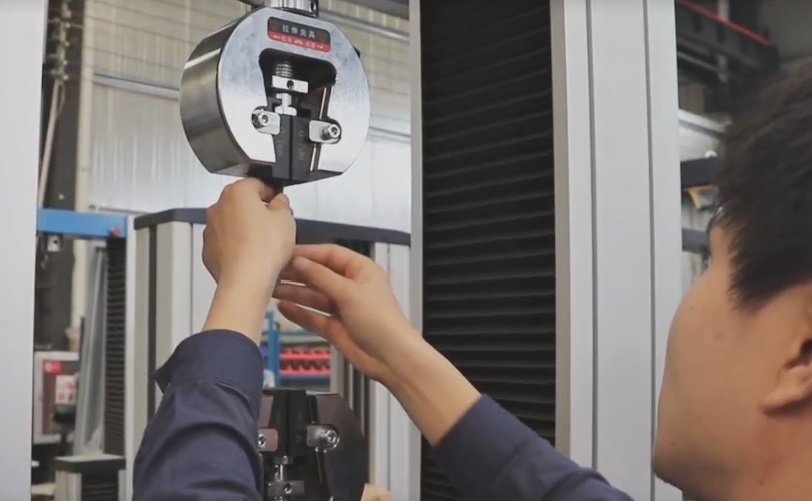
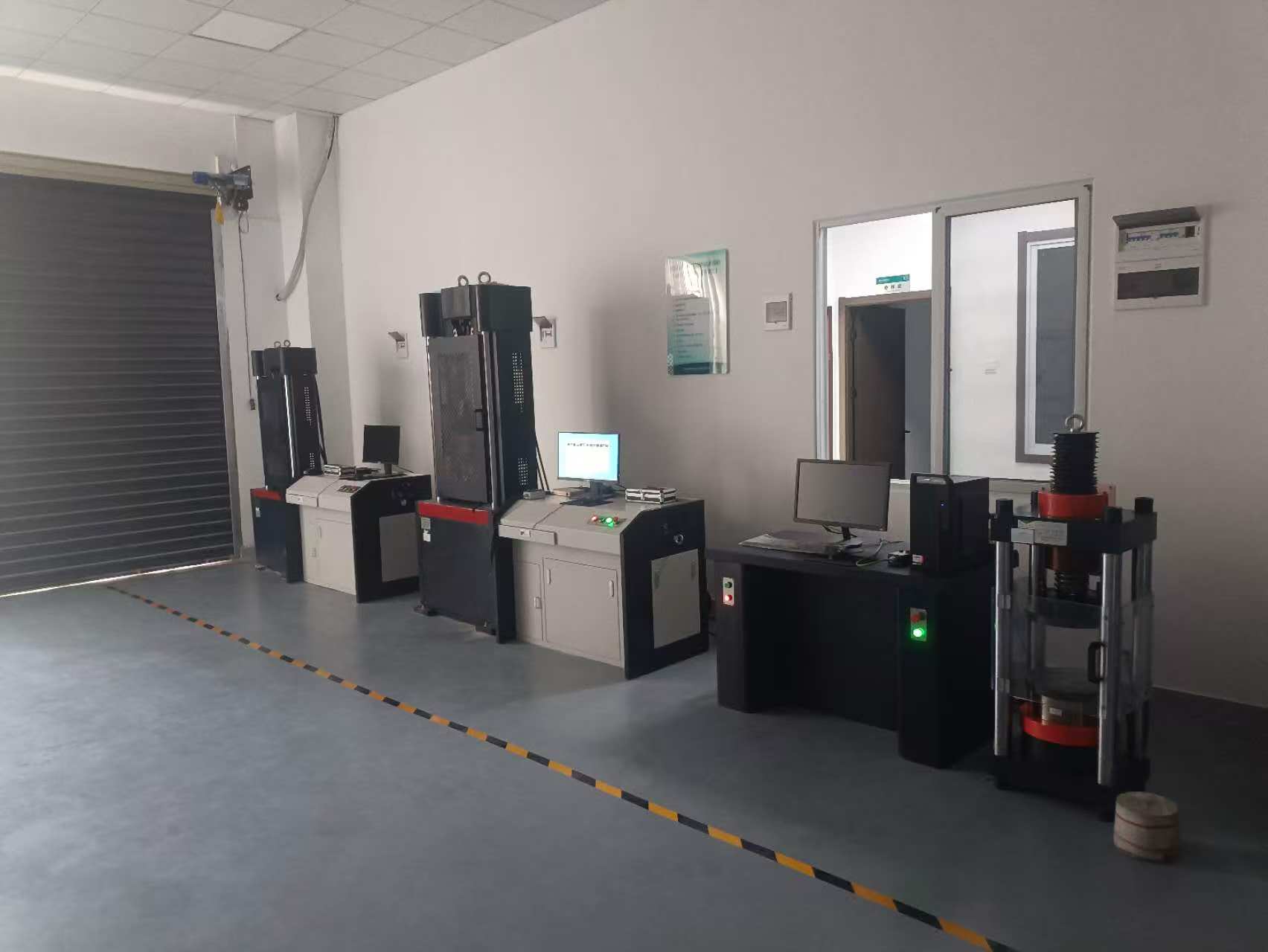
What Is Mechanical Testing Equipment?
Mechanical testing equipment refers to a broad range of machines and instruments used to evaluate the physical and mechanical properties of materials. These tests are essential in determining material performance under various conditions such as tension, compression, bending, impact, fatigue, and hardness. The results help engineers, researchers, and quality control professionals ensure product safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards such as ASTM, ISO, GB/T, and JIS.
From metals and plastics to composites and rubber, mechanical testing is critical in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, medical devices, and energy. As manufacturing becomes more complex and demanding, the need for accurate, automated, and efficient testing systems has grown substantially.
Common Types of Mechanical Testing Equipment
Depending on the testing requirements, mechanical testing equipment comes in many forms. Below are some of the most widely used types:
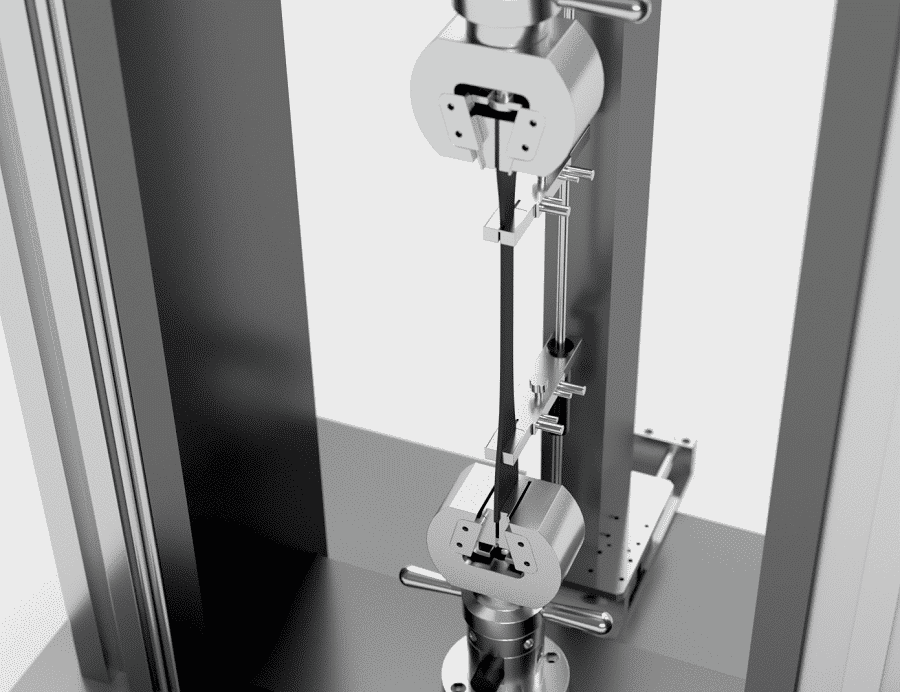
- Universal Testing Machines (UTMs): These versatile machines perform both tensile and compression tests. They can be electromechanical or hydraulic and are used across many industries for standard quality testing.
- Impact Testers: Used to determine a material’s ability to absorb energy during sudden loading, typically via Charpy or Izod methods.
- Hardness Testers: Measure a material’s resistance to indentation using methods like Rockwell, Vickers, and Brinell.
- Fatigue Testing Machines: Designed to test how a material behaves under cyclic loading. They’re essential in predicting service life.
- Torsion Testing Machines: Assess a material’s ability to withstand twisting forces, often used in wire, shaft, and tubing applications.
- Creep Testing Systems: Evaluate materials under long-term loading at elevated temperatures, critical in high-heat environments like aerospace or power generation.
- Compression and Flexural Testers: Common in concrete and plastics testing, they measure how a material performs under compression or bending forces.

Key Applications Across Industries
Mechanical testing equipment is not just for R&D labs; it plays a crucial role throughout the product development cycle. Here’s how different industries use mechanical testing:
- Automotive: Ensures components such as axles, seat frames, and airbag systems meet safety and performance standards.
- Aerospace: Tests composites, alloys, and fasteners under extreme conditions to guarantee flight safety.
- Construction: Evaluates the strength of concrete, steel, and geotextiles used in buildings and infrastructure.
- Medical Devices: Validates the durability and safety of implants, surgical tools, and prosthetics.
- Energy Sector: Used for testing turbine blades, oil pipelines, and nuclear components under thermal and mechanical stress.
How to Choose the Right Mechanical Testing Equipment
Choosing the right testing machine involves understanding your specific needs and matching them with the correct equipment capabilities. Here are key factors to consider:
- Test Type and Standards: Identify whether you need tensile, compression, fatigue, or other tests, and ensure the machine supports relevant standards (e.g., ASTM D638, ISO 6892).
- Material and Load Range: Know the range of materials you’ll be testing—plastics, metals, rubbers—and select appropriate load capacities.
- Control System and Software: Modern machines offer advanced control systems with customizable test parameters, automatic report generation, and digital data storage.
- Fixture Compatibility: Ensure the equipment allows for different grips, fixtures, and extensometers, especially if you’re testing diverse sample shapes.
- Automation and Throughput: If you’re handling high volumes or repetitive testing, automated systems with robotic handling or barcode scanning can drastically improve efficiency.
- Budget and ROI: Consider long-term maintenance, support, and upgrade options. Investing in high-quality equipment reduces downtime and increases test accuracy over time.
Trends and Innovations in Mechanical Testing
As digital transformation continues to shape every industry, mechanical testing is no exception. Here are some notable trends:
- Digital Twin Integration: Using real-world testing data to enhance virtual simulations in product design.
- AI-Powered Predictive Analysis: Leveraging machine learning to predict failure points and extend product life.
- IoT-Enabled Testing Systems: Remote monitoring, cloud storage, and real-time diagnostics are becoming standard features.
- Sustainability Focus: More companies are using testing to minimize material waste and develop eco-friendly alternatives.
Conclusion: Invest in Quality Testing for Long-Term Success
Mechanical testing equipment is a foundational element in modern manufacturing and research. Whether you’re ensuring product safety, validating materials, or optimizing performance, the right testing solution can save time, reduce costs, and enhance product reliability.
If you’re looking to upgrade or expand your testing capabilities, start by defining your test goals, understanding relevant standards, and consulting with an expert provider. With the right equipment in place, you’ll be well-equipped to meet quality demands today—and innovate for tomorrow.









