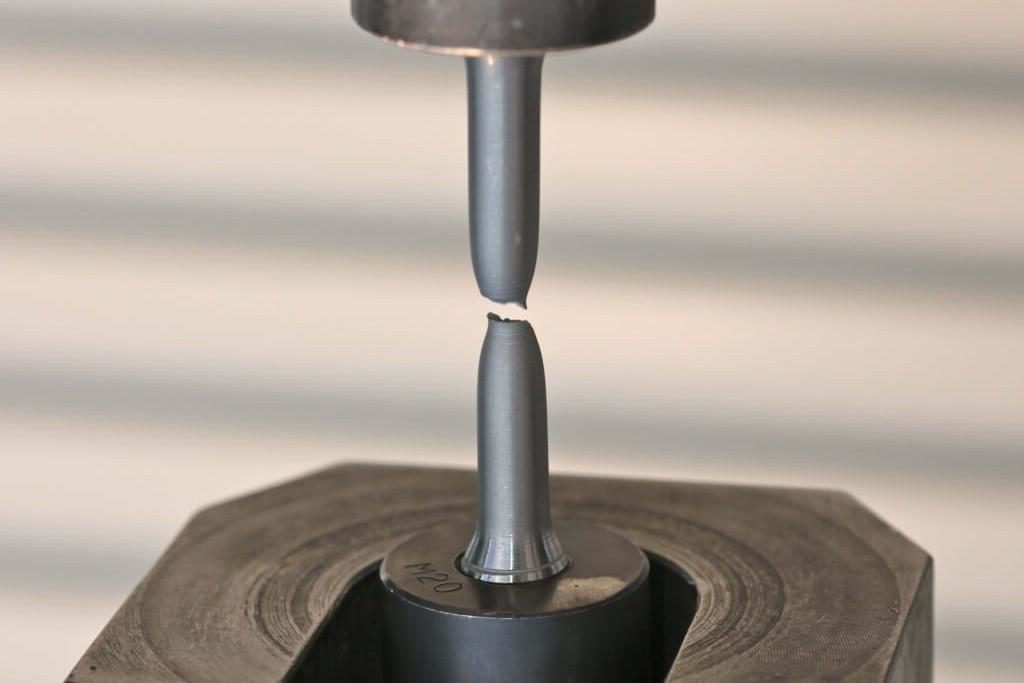
What is a tensile testing machine?
A tensile testing machine (also known as a universal material testing machine) is a test device used to measure the changes in physical properties of materials under mechanical loads such as tension, compression, and bending. The equipment can automatically complete the collection and calculation of parameters such as force, displacement, stress, strain, elastic modulus, yield strength, and elongation at break according to different standards, such as GB (China National Standard), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), etc.
According to different drive modes, tensile testing machines are divided into two categories: **electronic universal testing machines (servo motor drive) and hydraulic universal testing machines (hydraulic cylinder drive). The former is more suitable for medium and low load high-precision testing, and the latter is more suitable for large-tonnage metal material testing.
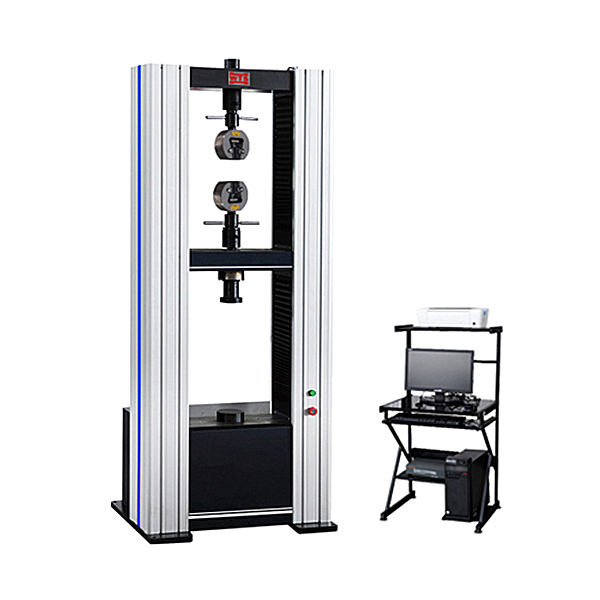

Working principle of tensile testing machine
The tensile testing machine is mainly composed of four parts: host structure, sensor system, drive control system, and data acquisition and analysis software.
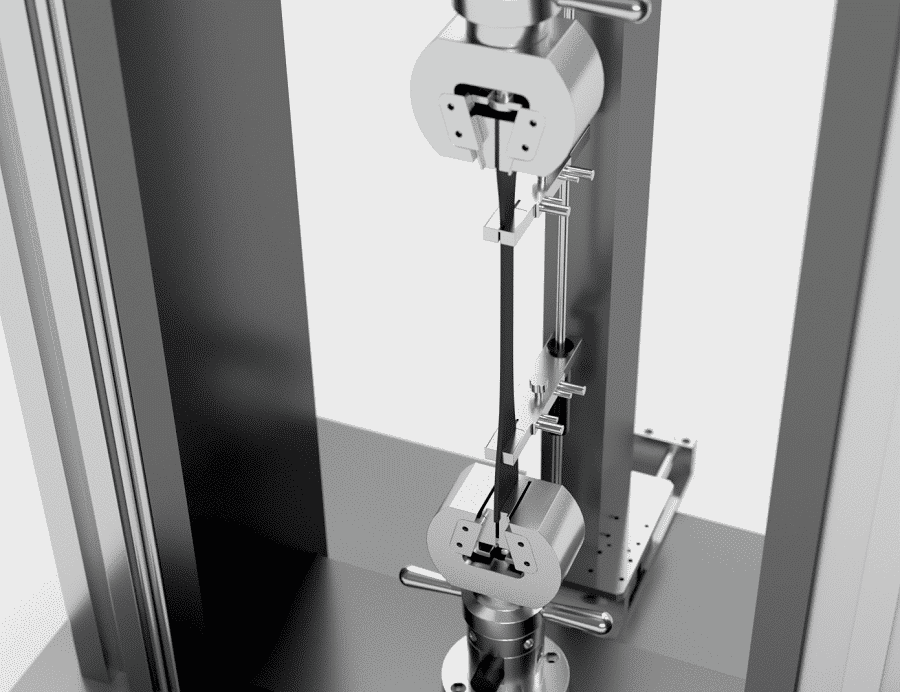
Host structure: including beams, screws, loading devices, and sample fixtures, which are the main structures for applying loads.
Sensor system: commonly used force sensors, displacement sensors, extensometers, etc., are used to detect key parameters such as load and deformation.
Drive control system: control the sample movement speed and loading process through servo motors or hydraulic cylinders to achieve precise control.
Data acquisition system: with computer software, it can display load-displacement or stress-strain curves in real time, and analyze and generate reports.
When the test starts, the sample is gradually stretched or compressed, the system records the corresponding force value and deformation, and draws a complete test curve, so as to judge the material’s elastic limit, yield point, tensile strength and other performance indicators.
Application fields of tensile testing machines
Due to its strong versatility, tensile testing machines are widely used in the following industries:
Metal material testing: such as tensile performance testing of steel bars, aluminum alloys, copper materials, etc.
Rubber and plastic industry: testing elongation at break, tensile strength, modulus
Textile and clothing: used for pull-off strength testing of cloth, wire, and buttons
Automobile and aerospace: evaluation of structural materials, welded joints, bonding strength, etc.
Building materials field: such as bending and tensile performance testing of wood, PVC pipes, and composite panels
Scientific research institutions and third-party laboratories: conduct new material development and material comparative analysis

Steps for using tensile testing machines
The standard tensile test process usually includes the following steps:
Equipment preparation: Check whether the power connection, data cable, and sensor are normal, and turn on the test system.
Fixture installation: Select a suitable fixture according to the size of the specimen and fix it. Common fixtures include wedge fixtures, pneumatic fixtures, roller fixtures, etc.
Specimen installation: Install the upper and lower ends of the specimen in the fixture to ensure that the axis is aligned to avoid bending loading.
Parameter setting: Enter parameters such as sample size, loading speed, and termination conditions in the software.
Start the test: Click “Start”, the system automatically performs loading and records data in real time.
Observe the curve: Determine the change in material performance based on the force-displacement or stress-strain curve.
Report output: Automatically generate a report after the test, including charts, key indicators, notes, etc.
Maintenance recommendations for tensile testing machines
To ensure long-term stable operation of the equipment, the following daily maintenance items should be noted:
Regularly calibrate the sensor to ensure test accuracy
Clean the lead screw and guide rail regularly and add lubricating oil
Clean the fixture in time after use to prevent rust or jamming
The software regularly backs up test data to avoid loss
Hydraulic system equipment should check the oil level, filter and leakage
The storage environment should be dry and free of corrosive gases to prevent damage to electronic components