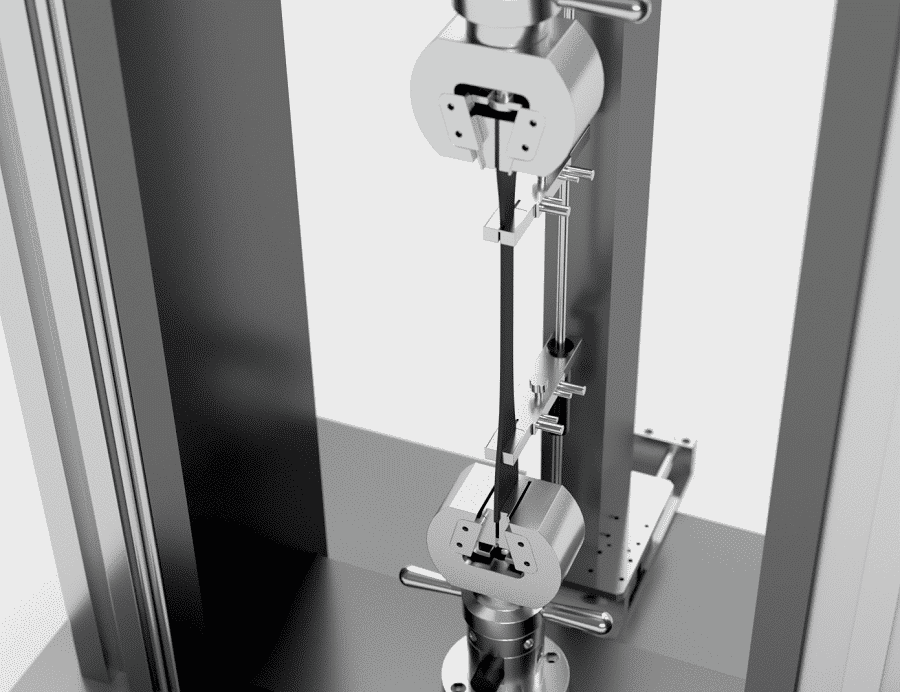
In today’s competitive manufacturing environment, ensuring material quality and performance is more critical than ever. A Universal Testing Machine (UTM) plays a vital role in this process. Also known as a materials testing machine or tensile tester, a UTM is essential for testing the mechanical properties of metals, plastics, composites, and other materials. This article will explore what a UTM is, how it works, and why it’s crucial across industries.
What Is a Universal Testing Machine?
A Universal Testing Machine is a type of mechanical testing equipment designed to perform a wide range of tests on materials. These typically include:
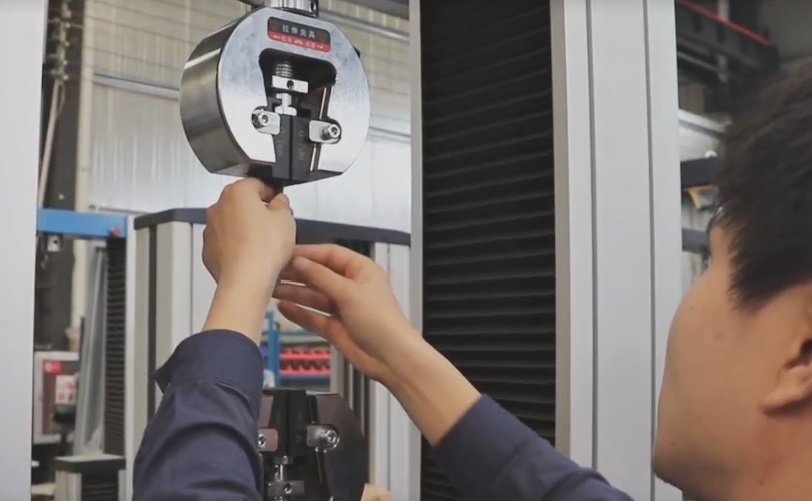
- Tensile testing (pulling)
- Compression testing (pushing)
- Bending/flexural testing
- Shear testing
- Peel and tear testing
The term “universal” comes from the machine’s ability to adapt to different test methods by changing fixtures and settings. UTMs can be controlled manually or digitally through software, providing precise force-displacement data for quality assurance and product development.

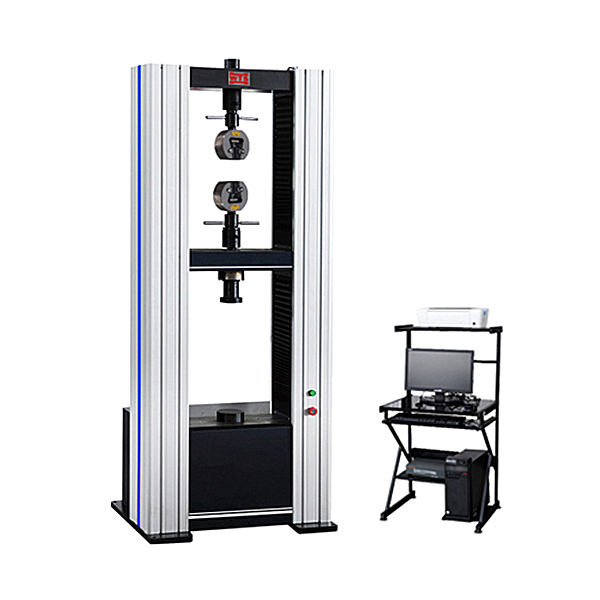
Key Components of a UTM
A standard Universal Testing Machine consists of:
Load frame: The main structure with crossheads that move to apply force.
Load cell: Measures the force applied to the specimen.
Grips/fixtures: Hold the test specimen in place.
Controller/software: Manages test parameters and records data.
UTMs come in two main types: electromechanical (screw-driven) for low to medium loads, and hydraulic for high-capacity applications such as metal or concrete testing.
Why Use a Universal Testing Machine?
Whether you’re manufacturing automotive components, aerospace structures, or consumer products, materials must meet strict performance standards. A UTM allows manufacturers to:
Validate material strength and durability
Ensure compliance with international standards (ASTM, ISO)
Improve product safety and performance
Optimize material selection and design
In industries like construction, defense, and biomedical engineering, failure to test materials properly can lead to safety hazards, recalls, and financial loss.
Applications Across Industries
Universal Testing Machines are widely used in:
- Metallurgy: For testing steel, aluminum, and alloys
- Plastics & Polymers: Tensile and elongation properties
- Textile & Leather: Tear, seam, and tension strength
- Rubber & Elastomers: Modulus, compression, and fatigue
- Construction Materials: Concrete, rebar, and cement
From R&D laboratories to production lines, UTMs provide the data needed to make informed engineering and business decisions.

Choosing the Right UTM for Your Needs
When selecting a UTM, consider:
- Force capacity (e.g., 5 kN to 1000 kN)
- Test types required
- Speed and precision
- Software capabilities
- Compliance with ASTM/ISO standards
Leading manufacturers offer modular systems with customizable fixtures and advanced reporting tools, enabling seamless integration into quality management systems.
Final Thoughts
A Universal Testing Machine is not just a piece of lab equipment — it is a strategic investment in product reliability, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. As material science continues to evolve, the importance of accurate and efficient mechanical testing will only grow.
Whether you’re upgrading an existing lab or setting up a new facility, choosing the right UTM can help you stay ahead in a competitive global market.